Patent Translation - Fast and Accurate
Translations for all languages with any file type support, get your fast translation!


Intellectual property (IP) refers to creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, and symbols, names, and images used in commerce. IP is protected by laws, which vary from country to country. Some examples of IP that might need translation into foreign languages include:
There are many other forms of IP that might need translation into foreign languages, depending on the nature of your business and your international activities.
DocTranslator is a sophisticated online translation service that allows users to upload various document formats, including Word, PDF, and PowerPoint, and have them translated into different languages. Leveraging the power of the Google Translate engine, DocTranslator is specifically designed for documents and includes extra features that make it more suitable for this purpose compared to standard translation services.
Patent translation is the process of translating a patent or patent application from one language to another. Patents are legal documents that protect new and useful inventions. They typically include a written description of the invention and its intended use, as well as one or more claims that define the scope of the protection afforded by the patent.
Patent translation is a specialized field that requires a high level of technical expertise and a thorough understanding of patent law. Patent translators must be able to accurately convey the technical details of the invention and the legal requirements of the patent system in the target language. They must also be able to use the appropriate technical terminology and legal terminology in the translation.
Patent translation is often required when an inventor or company wants to obtain a patent in a foreign country. In order to do this, they must file a patent application in the local language. The patent application must be complete and accurate, and the translation must be of high quality in order to be accepted by the patent office. Patent translation is also sometimes needed for litigation purposes, when a patent holder needs to present their patent in a foreign language.
Patents, trademarks, and copyrights are all forms of intellectual property (IP) that protect different types of creations of the mind. Here is a brief overview of the main differences between these three types of IP:
Patents: Patents are legal documents that protect new and useful inventions. They typically include a written description of the invention and its intended use, as well as one or more claims that define the scope of the protection afforded by the patent. Patents are granted by the government and are typically valid for a limited period of time, usually 20 years from the date of application.
Trademarks: Trademarks are words, phrases, symbols, or designs that are used to identify and distinguish a particular product or service from those of others. Trademarks can be registered with the government or acquired through use. A registered trademark is typically valid for 10 years and can be renewed indefinitely as long as it is being used in commerce.
Copyrights: Copyrights protect literary, artistic, and other creative works, such as books, music, and software. Copyrights are typically granted automatically as soon as a work is fixed in a tangible form, such as when it is written down or recorded. In most countries, copyrights last for the life of the creator plus a certain number of years after their death.
In summary, patents protect inventions, trademarks protect branding, and copyrights protect creative works. Each type of IP has its own specific legal requirements and protections, and it is important to understand the differences between them in order to properly protect your intellectual property.
To become a patent translator, you will typically need to have at least a bachelor’s degree in a technical or scientific field, as well as a high level of proficiency in both the source language (the language the patent is written in) and the target language (the language you will be translating into). In addition to your educational background, it is also important to have a strong understanding of patent law and the terminology used in patents.
Some companies and individuals who offer patent translation services may also require that you have professional certification, such as the American Translators Association’s (ATA) Certified Patent Translator credential. This certification is obtained through a combination of education, experience, and successful performance on a written and oral exam.
As for how much you can expect to make as a patent translator, it will depend on a variety of factors, including your level of education and experience, the demand for your language combination, and the complexity of the patents you are translating. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for translators and interpreters in the United States was $52,830 in 2020. However, it is important to note that this figure includes all types of translators and interpreters, not just those specializing in patent translation.
The cost of translating a patent can vary widely depending on a number of factors, including the length of the patent, the complexity of the technology involved, the languages involved, and the turnaround time. Some companies and individuals may offer lower rates for patent translation, but it is important to keep in mind that the quality of the translation may suffer if the translator is not experienced or proficient in the technical and legal terminology used in patents.
On average, you can expect to pay anywhere from $0.10 to $0.30 per word for patent translation. For a patent application with around 20,000 words, this would come out to a total cost of between $2,000 and $6,000. However, it is important to get quotes from several different translation companies or translators in order to get an accurate estimate of the cost for your specific project.
DocTranslation boasts impressive user engagement metrics, with over 80% of first-time users returning for future translations. Additionally, our platform maintains a high satisfaction rate, with 95% of customers rating their experience as excellent or good. The average session duration continues to grow, reflecting the ease of use and trust our users place in the platform's quality and reliability.
DocTranslation facilitates meaningful cross-cultural communication through thousands of daily conversations. The platform processes more than 20,000 unique translation requests each day, spanning documents in multiple formats. This robust daily activity demonstrates DocTranslation’s capacity to handle high volumes efficiently, helping individuals and businesses bridge language barriers smoothly.
DocTranslation's cutting-edge AI translation engine is powered by vast training data, with billions of words sourced from diverse, multilingual datasets. This extensive training data enables our system to understand nuanced language structures and idiomatic expressions, resulting in translations that are both contextually accurate and culturally sensitive. Such comprehensive training ensures that users receive consistently high-quality translations across all languages supported.
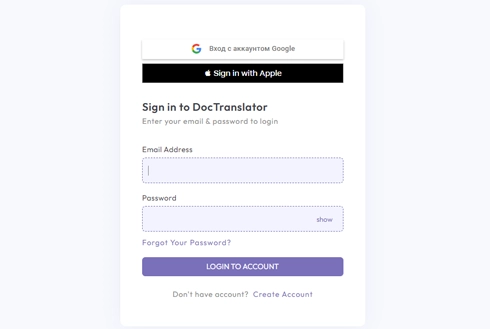
Begin your translation journey by setting up a free account on our platform. It only takes a few moments to provide your basic information and confirm your email address. This account will serve as your personalized hub for uploading, tracking, and managing all your translation projects.
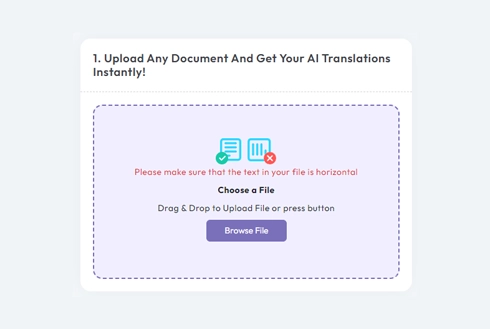
After logging in, it's time to upload your document. Our system supports a wide variety of formats, including MS Word, Excel, PowerPoint, TXT, InDesign, and CSV. Simply drag and drop your file or use the “Browse” option to select the file from your device.
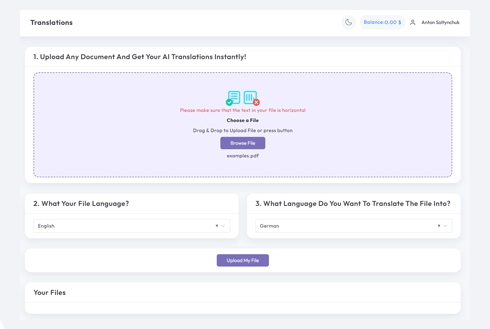
Specify the language in which your original document is written. Then, choose the target language to which you want the document translated. With our extensive list of supported languages, you'll find the perfect match for your audience, whether it's for a business proposal or a creative campaign.
Once you've set your language preferences, click the “Upload” button to begin processing. Sit back and relax while our advanced translation system works on your file, maintaining the original layout and style while delivering an accurate translation.
Select a File